Contents
Ovarian cancer is a complex disease that frequently remains undetected until it reaches advanced stages, underscoring the importance of awareness regarding its symptoms.
What are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer? This article examines the common signs that may indicate ovarian cancer, explores the associated risk factors, and discusses the varying survival rates at different stages of the disease.
It also addresses the available treatment options and preventive measures that can mitigate the risk of developing this serious condition.
A thorough understanding of these aspects can give the power to individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer manifests a variety of symptoms that can profoundly impact a patient’s quality of life, underscoring the importance of early detection in improving overall survival rates and prognoses.
Symptoms such as abdominal bloating, pelvic pain, and alterations in bowel habits may present subtly and are frequently misattributed to other medical conditions, thereby complicating the diagnostic process.
Consequently, a comprehensive understanding of these symptoms can give the power to individuals to pursue timely medical intervention from healthcare professionals, thereby enhancing the likelihood of successful treatment options and subsequent follow-up care.
1. Abdominal bloating
Abdominal bloating is a prevalent and often distressing symptom encountered by women with ovarian cancer, characterized by a sensation of fullness or swelling in the abdominal area.
This sensation can be particularly troubling, as it may hinder daily activities and obscure other symptoms that could indicate the disease’s progression.
In contrast to benign causes of bloating, such as dietary factors or gastrointestinal disorders, bloating associated with ovarian cancer typically results from the tumor’s impact on the abdominal cavity and surrounding organs.
This distinction emphasizes the importance of women experiencing persistent bloating to seek medical consultation without delay.
Differentiating between bloating caused by benign factors and that linked to cancer can be challenging.
Therefore, it is essential for healthcare professionals to assess the persistence and context of the symptom, ultimately facilitating timely diagnosis and effective management.
Early intervention can significantly improve what are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer.
2. Pelvic pain
Pelvic pain in patients with ovarian cancer can vary from mild discomfort to severe pain, often manifesting as a persistent issue that may signify underlying malignancy.
This type of pain can fluctuate in intensity, occasionally exacerbating during specific activities or at certain times of the month. It may also be accompanied by additional concerning symptoms such as bloating or changes in appetite.
As a significant symptom, pelvic pain requires careful consideration, particularly in relation to various risk factors, including age, family history, and genetic predisposition.
Individuals experiencing these symptoms are strongly encouraged to pursue comprehensive medical evaluations to rule out potential issues, including ovarian cancer.
Early diagnosis can substantially influence treatment outcomes, highlighting the necessity of monitoring any abnormal or persistent pelvic discomfort.
3. Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly
Numerous women diagnosed with ovarian cancer report experiencing difficulty with eating or feeling satiated quickly, which can significantly affect their nutritional intake and overall quality of life.
This symptom frequently results in inadequate caloric consumption, thereby undermining their nutritional status and complicating their ability to manage the physical demands associated with cancer treatment.
Maintaining proper nutrition during this critical period is essential, as it can influence the efficacy of treatment, the recovery process, and overall well-being.
Nutritional deficiencies can compromise the immune system and diminish the body’s capacity to cope with the side effects of therapies such as chemotherapy or radiation.
Consequently, implementing effective symptom management strategies that address appetite-related issues is crucial, ensuring that these individuals receive the necessary nourishment to support their health and sustain energy throughout their treatment journey.
4. Changes in bowel habits
Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhea, can serve as significant indicators of ovarian cancer and warrant prompt consultation with healthcare providers.
These alterations in digestive patterns may arise from the physical presence of a tumor that affects nearby intestinal structures or disrupts normal hormonal functions.
The complex biological interplay between ovarian function and gastrointestinal health can result in changes that manifest in unexpected ways, highlighting the intricate nature of the human body.
Given that these symptoms may frequently be dismissed or attributed to less serious conditions, it is essential for individuals to proactively engage in discussions with their healthcare professionals.
This ensures that any concerning signs are thoroughly investigated to rule out serious underlying issues.
5. Frequent urination
Frequent urination may be an often-overlooked symptom of ovarian cancer, frequently resulting in discomfort and emotional distress among patients.
This symptom can have a significant impact on a patient’s daily life, as the persistent need to use the restroom can disrupt work, social engagements, and personal moments, leading to feelings of isolation and anxiety.
The necessity to manage this issue can further contribute to the physical and emotional challenges already faced by individuals battling the disease.
Therefore, it is crucial for those experiencing these difficulties to seek emotional support from friends, family, or support groups, as this can help mitigate feelings of loneliness.
Additionally, employing coping strategies such as pelvic floor exercises and mindfulness techniques can give the power to patients, enabling them to regain a sense of control over their bodies and lives amid the uncertainties associated with ovarian cancer.
Understanding and addressing these symptoms can improve the odds of early detection and successful treatment, directly impacting what are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer.
By being informed about the symptoms of ovarian cancer and seeking timely medical advice, individuals can enhance their chances of survival and better manage their health.
What are the risk factors for ovarian cancer?
Understanding the risk factors associated with ovarian cancer is crucial for facilitating early detection and implementing effective prevention strategies.
Several factors, including age, family history, and inherited gene mutations, can significantly affect a woman’s likelihood of developing this condition.
Age is a critical factor, as the risk for ovarian cancer increases with advancing years, particularly after the age of 50.
Furthermore, a family history of breast or ovarian cancer may heighten concerns, necessitating discussions regarding genetic testing and potential preventive measures.
1. Age
Age is a significant risk factor for ovarian cancer, with statistics indicating that the majority of cases are diagnosed in women over the age of 50.
This correlation can be attributed to various biological factors that increase the risk as women age, including hormonal changes and a decline in genetic repair mechanisms.
Research indicates that women in their 60s have a notably higher incidence rate, with over 50% of cases detected within this demographic.
Understanding what are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer is closely tied to early detection, which becomes more challenging as women age. While the efficacy of screening methods remains a topic of debate, they are critical for early detection, particularly in older populations.
Regular check-ups and awareness of symptoms can significantly improve outcomes, highlighting the necessity of targeted screenings for individuals within this age group.
2. Family history
A robust family history of ovarian or breast cancer can substantially elevate a woman’s risk of developing ovarian cancer, primarily due to genetic predisposition.
This familial association underscores the necessity of proactive risk assessment, particularly in recognizing how inherited mutations, such as those present in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, can affect an individual’s likelihood of developing these diseases.
As a result, genetic testing provides valuable insights for individuals with a family history of these cancers, give the power toing them to make informed decisions regarding their health.
These genetic factors can significantly influence discussions with health insurance providers, who may need to consider the necessity of covering preventive measures, such as regular screenings or even prophylactic surgeries.
Consequently, supportive family networks can serve as critical allies in navigating these complexities, fostering conversations that promote better health outcomes while emphasizing the importance of early detection and intervention.
3. Inherited Gene Mutations
Inherited gene mutations, particularly those involving the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, represent significant risk factors for ovarian cancer. This underscores the necessity for proactive risk assessment and the development of potential preventive strategies.
A comprehensive understanding of the genetic landscape enables women to make informed decisions regarding their healthcare.
Identifying these mutations extends beyond mere awareness – it facilitates the advancement of personalized medicine.
With genetic information in hand, healthcare providers can customize prevention strategies and treatment options, leading to significantly improved outcomes. Such an approach enhances monitoring and surveillance methods and helps in selecting appropriate therapies, ultimately giving women better control over their health and wellbeing.
This, in turn, can influence what are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer for those affected.
4. Hormone replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy has been linked to an increased risk of ovarian cancer, prompting women to carefully consider the benefits and risks associated with such treatments.
Understanding the complexities of this relationship is essential, particularly as many individuals seek relief from menopausal symptoms that can significantly affect their quality of life.
Women are encouraged to explore alternative therapies that may provide a safer approach to symptom management, including lifestyle modifications, herbal remedies, or non-hormonal medications.
Each of these options presents its own set of potential benefits and drawbacks, underscoring the importance of well-considered choices in light of the varying risk factors associated with ovarian cancer.
Engaging in discussions with healthcare providers regarding individualized risks can facilitate a more comprehensive approach to women’s health and offer a clearer perspective on what are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer.
What are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer, often dubbed the “silent killer” due to its subtle and frequently undetectable symptoms, represents a significant health challenge for women globally. This moniker underscores the difficulty in identifying the disease at an early stage, which can greatly influence survival rates.
To truly understand the odds of surviving ovarian cancer, it is essential to examine a variety of factors that contribute to a patient’s prognosis. Key elements include the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed, the specific type of ovarian cancer present, and the effectiveness of the treatments administered.
Accurate assessment of survival odds involves evaluating how these factors interplay, which can provide a clearer picture of a patient’s potential outcomes and the various strategies that might enhance their chances of survival.
What are the survival rates for ovarian cancer?

Survival rates for ovarian cancer fluctuate considerably depending on the stage of the disease at the time of diagnosis, with early detection being crucial for enhancing prognosis and patient outcomes.
The five-year survival rate for early-stage ovarian cancer can surpass 90%, whereas advanced stages demonstrate a significant decrease in survival statistics. This disparity highlights the necessity of awareness campaigns and routine health screenings.
A comprehensive understanding of these survival statistics can assist patients and their families in making informed decisions regarding treatment options and participation in clinical trials. Knowing what are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer at various stages helps in tailoring a more effective and personalized treatment plan.
Stage 1
Stage 1 ovarian cancer is defined by the presence of tumors that are confined to the ovaries, and survival rates are significantly higher in this stage compared to later stages, highlighting the critical importance of early detection.
When diagnosed at this initial stage, patients often experience an impressive five-year survival rate that can exceed 90%.
Treatment options generally involve a combination of surgical intervention to remove the ovaries, with chemotherapy employed as necessary based on the individual case.
It is essential for patients to recognize that while the prognosis is favorable with early diagnosis, the journey toward recovery does not conclude there.
Consistent follow-up care is imperative for monitoring recovery and detecting any potential recurrence.
This underscores the necessity of a comprehensive care plan that includes regular check-ups and imaging as recommended by their healthcare team.
Stage 2
Stage 2 ovarian cancer signifies that the cancer has metastasized to nearby pelvic organs while remaining localized. This condition still permits favorable survival rates when appropriate treatment measures are implemented.
Patients confronting this diagnosis may evaluate a variety of treatment options aimed at effectively addressing the illness. Surgical intervention is often the initial approach, with the objective of excising as much of the tumor as possible.
Post-surgery, chemotherapy typically assumes a critical role in targeting any residual cancer cells, thereby improving long-term prognoses.
Individuals diagnosed with stage 2 ovarian cancer should also consider participating in clinical trials, as these studies may provide access to innovative therapies and contribute to advancements in medical science.
Furthermore, support systems comprising family and friends can significantly enhance emotional well-being during treatment, which is vital for navigating this arduous journey.
Stage 3
Stage 3 ovarian cancer is characterized by considerable dissemination within the abdominal cavity, resulting in significantly reduced survival rates and an increased risk of recurrence following treatment.
Understanding what are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer at this stage involves recognizing the challenges that complicate effective treatment.
Patients may encounter a range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, and alterations in bowel habits, which can impede timely diagnosis and prompt intervention.
Treatment options are generally multifaceted, typically commencing with surgical intervention aimed at excising as much tumor mass as possible. This is usually followed by chemotherapy to target residual cancer cells and minimize the likelihood of recurrence.
The response to treatment can vary markedly among patients, underscoring the importance of patients and their families advocating for their needs and preferences throughout the care process.
A comprehensive understanding of prognosis, along with consideration of the emotional and psychological dimensions of treatment, can give the power to individuals and ultimately contribute to the development of more personalized and effective care plans.
Stage 4
Stage 4 ovarian cancer represents the most advanced stage of the disease, characterized by metastasis to distant organs.
This stage is associated with the lowest survival rates, necessitating a shift in focus towards palliative care aimed at enhancing the quality of life for patients.
At this critical juncture, treatment strategies prioritize the alleviation of symptoms and the maximization of comfort rather than curative intent.
Patients often face a multitude of challenges, including pain management and emotional distress, which underscores the importance of supportive care.
A range of therapeutic modalities, including chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and medications for symptom relief, are utilized to manage adverse effects and improve daily functioning. Additionally, holistic approaches such as counseling and support groups can provide essential emotional support for patients and their families.
This integrative care not only addresses the psychological impact of the diagnosis but also fosters resilience, enabling individuals to navigate this journey with dignity and the potential for joy.
Understanding what are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer at each stage can guide patients and their families in making informed choices about their care and improving overall outcomes.
How is ovarian cancer treated?
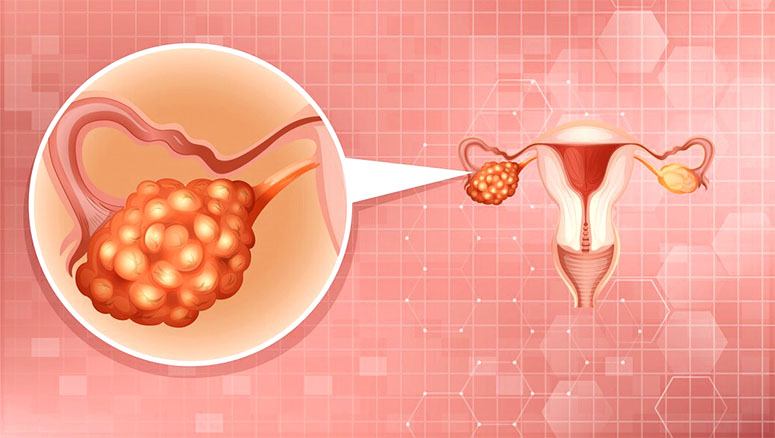
Treatment options for ovarian cancer are comprehensive and generally consist of a combination of surgical intervention, chemotherapy, and, in certain cases, radiation therapy, all tailored to the stage of cancer and the specific needs of the patient.
Surgical intervention is primarily focused on the maximal removal of the tumor, which is often followed by chemotherapy to address any residual cancer cells.Additionally, the treatment plan may incorporate personalized medicine strategies informed by genetic testing, aimed at improving treatment efficacy and reducing potential side effects.
1. Surgery
Surgical intervention is frequently the primary treatment strategy for ovarian cancer, with the goal of excising as much of the tumor as possible while evaluating the extent of the disease.
This initial procedure typically involves a hysterectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy, allowing for a comprehensive examination of surrounding tissues and lymph nodes.
The main objectives of this surgery are to eradicate cancerous cells and assess whether the cancer has metastasized, which will subsequently influence treatment protocols.
What are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer after surgery? The success largely depends on how effectively the cancer is removed and whether there are residual cancer cells remaining.
Treatment options may include:
- Debulking surgery, which aims to reduce tumor size;
- Exploratory surgery, intended to obtain critical diagnostic information.
Recovery expectations may vary – however, patients generally undergo a hospital stay followed by a gradual return to their regular activities.
This process underscores the vital role of an oncologist, who provides guidance to patients regarding the complexities of surgical options, customizing a treatment approach that considers both overall health and the specific characteristics of the cancer.
2. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a vital component in the treatment of ovarian cancer, typically administered post-surgery to eliminate any residual cancer cells and diminish the risk of recurrence.
This strategy not only seeks to enhance overall survival rates but also aims to improve the quality of life for individuals affected by the disease.
Various chemotherapy regimens, which are specifically tailored to each patient’s unique circumstances, may include combinations of drugs such as carboplatin and paclitaxel.
These regimens have demonstrated considerable efficacy in managing the disease – however, patients may encounter a range of common side effects, including fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
Therefore, it is imperative for patients to receive comprehensive education regarding their treatment options and the necessity of strict adherence to prescribed protocols, as these factors can significantly impact the likelihood of a favorable outcome.
3. Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is occasionally employed in the treatment of ovarian cancer, particularly to target specific areas in cases of recurrent disease or advanced stages of cancer where surgical options are limited.
This modality is an essential component of the overall treatment plan, especially for patients experiencing localized symptoms that may not be adequately managed through other interventions.
It can significantly contribute to palliative care, with the aim of not only prolonging life but also enhancing the quality of life by alleviating pain and discomfort associated with tumor progression.
While the primary objective remains the relief of symptoms, it is important to acknowledge that potential side effects such as fatigue, skin irritation, and abdominal discomfort may occur, necessitating careful monitoring by healthcare professionals.
A thorough understanding of these factors enables a more comprehensive approach to managing ovarian cancer, particularly in patients for whom curative therapies are not feasible.
4. Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy has emerged as a promising treatment option for ovarian cancer, concentrating on specific molecular targets associated with the disease.
This approach has the potential to enhance treatment efficacy while minimizing the impact on healthy cells.
What are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer with targeted therapy? This innovative methodology employs advanced techniques to identify genetic mutations and alterations within cancer cells, facilitating the development of more personalized treatment strategies.
By focusing on the unique characteristics of each tumor, healthcare providers can customize interventions that are more likely to yield successful outcomes, thereby offering patients hope for improved prognoses.
The advantages of targeted therapy are further bolstered by ongoing medical research, which underscores the critical role of clinical trials in assessing new agents and treatment combinations.
Equally essential is patient education, ensuring that individuals have access to information regarding emerging therapies and the significance of participation in these important studies, thus give the power toing them throughout their treatment journey.
How can ovarian cancer be prevented?
Preventative measures for ovarian cancer concentrate on addressing recognized risk factors and promoting lifestyle modifications that may reduce the incidence of this malignancy.
Regular health screenings and awareness campaigns are essential for facilitating early detection, while lifestyle changes—such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and judiciously considering hormonal treatments – can significantly contribute to risk reduction.
Additionally, education regarding family history and genetic predispositions can further give the power to women to make informed decisions regarding their health.
1. Oral contraceptives
The use of oral contraceptives has been linked to a decreased risk of developing ovarian cancer, making this an important factor in prevention strategies for women, particularly those with a family history of the disease.
This association underscores the significance of understanding the various risk factors that contribute to cancer development.
Women with a familial predisposition to ovarian cancer may consider incorporating hormonal contraceptives as a proactive measure to mitigate their risk.
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in patient counseling by discussing these protective effects, while also emphasizing the necessity of individualized approaches based on each patient’s medical history and lifestyle.
Informed decision-making is crucial as women evaluate the benefits of contraception against potential side effects, ensuring they possess a comprehensive understanding of their options and the implications for their long-term health.
2. Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Evidence indicates that pregnancy and breastfeeding may reduce the risk of ovarian cancer, likely due to hormonal changes and a decrease in ovulation cycles during these periods.
This protective effect appears to arise from the manner in which these life stages affect hormonal balance and limit the frequency of ovulation.
During pregnancy, an individual’s body experiences significant hormonal fluctuations that may result in a decreased overall number of menstrual cycles.
This reduction is believed to diminish the ovaries’ exposure to potential carcinogens released during ovulation.
Moreover, breastfeeding plays a crucial role, as it not only extends the interval between pregnancies but also modifies hormonal levels in a way that could impede the development of ovarian tumors.
Such findings underscore the significance of lifestyle choices, highlighting that decisions related to childbearing can have substantial implications for long-term health and cancer risk, ultimately influencing what are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer.
3. Tubal ligation
Tubal ligation has been recognized as a potential preventive measure against ovarian cancer, as it may reduce the risk by interrupting the pathway through which cancerous cells could reach the ovaries.
This surgical procedure not only serves as a significant intervention for individuals seeking to manage their reproductive choices but also prompts a broader discussion regarding women’s health and well-considered choices.
Understanding the effectiveness of tubal ligation underscores its importance within a woman’s overall health strategy.
It is crucial for individuals to consider the potential risks associated with the procedure, including complications, hormonal changes, and the possibility of regret should future fertility be desired.
Women can give the power to themselves by thoroughly evaluating these risk factors and consulting with healthcare professionals, ensuring that their choices are in alignment with their reproductive goals and health needs.This comprehensive approach can also impact what are the odds of surviving ovarian cancer, as preventive measures are integral to improving long-term outcomes.
Visit our FAQ section lower on the page to discover more about ovarian cancer survival statistics.
Explore the captivating world of probabilities and uncommon events. Satisfy your curiosity and discover more fascinating topics by visiting our other articles at WhatAreTheOddsOf.NET.



