Contents
Herpes is a prevalent viral infection that affects millions of individuals worldwide, yet it remains surrounded by numerous misconceptions.
Many people wonder what are the odds of getting herpes? Understanding the factors that influence transmission can help clarify this question.
A comprehensive understanding of herpes begins with recognizing its types, primarily Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 and 2, as well as the Varicella-Zoster Virus.
This article aims to elucidate the modes of transmission associated with herpes, the symptoms that individuals should monitor, and the risk factors that may elevate the likelihood of contracting the virus.
Additionally, practical recommendations for minimizing risk will be provided. By equipping oneself with this essential knowledge, individuals can make informed health decisions.
What Is herpes ?
Herpes is a prevalent viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), affecting millions of individuals globally and resulting in various manifestations of the disease, including oral herpes and genital herpes.
It is essential to understand the different types of herpes, their transmission routes, and relevant statistics to facilitate effective prevention and management.
The symptoms of herpes can vary widely, ranging from mild to severe, and a significant number of individuals may remain asymptomatic or unaware of their condition, which contributes to its status as a common sexually transmitted infection (STI).
What are the types of herpes?
The herpes family of viruses encompasses several types, primarily Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1) and Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2), in addition to the Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV), which is responsible for chickenpox and shingles.
A comprehensive understanding of these herpes types is crucial for effective prevention and management of outbreaks, as each virus exhibits distinct transmission routes and associated symptoms.
1. Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1)
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1) primarily causes oral herpes, which is characterized by painful blister-like sores or lesions on the lips and mouth, commonly referred to as cold sores.
Understanding the transmission routes of HSV-1, particularly through skin-to-skin contact, is essential for effective outbreak management and for reducing the risk of transmission to sexual partners.
The implications of HSV-1 extend beyond physical discomfort – they can significantly impact emotional well-being and interpersonal relationships.
Individuals affected by HSV-1 often experience recurring outbreaks, which may be triggered by factors such as stress, illness, or exposure to sunlight. Therefore, awareness of these triggers is crucial.
Risk factors for transmission include:
- sharing utensils;
- kissing;
- engaging in oral sexual activities while symptomatic.
Implementing prevention strategies, such as avoiding contact during outbreaks and utilizing antiviral medications, can substantially reduce these risks.
Access to healthcare is critical for individuals seeking diagnosis and treatment options, as enhanced awareness and education enable those affected to manage their condition effectively.
2. Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2)
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2) is primarily linked to genital herpes, which presents as painful genital lesions and can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life.
Understanding the transmission probability of HSV-2, particularly among sexual partners, is essential for evaluating STI risks and developing effective herpes prevention strategies.
Individuals affected by HSV-2 may experience recurrent outbreaks, which can vary in frequency and severity. Common symptoms include itching, burning sensations, and uncomfortable sores that may take weeks to heal.
There are numerous misconceptions surrounding HSV-2 – for instance, it is often assumed that the virus only transmits during visible outbreaks. However, asymptomatic shedding can also present a risk of transmission.
Consequently, fostering open communication regarding sexual health with partners is crucial.
Engaging in responsible behaviors, such as utilizing condoms and being aware of one’s herpes status, not only reduces the likelihood of transmission but also fosters a healthier and more transparent relationship.
Understanding these factors equips individuals with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of genital herpes with increased confidence and awareness.
3. Varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
The Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV) is a member of the herpesvirus family, primarily recognized for its role in causing chickenpox in children and shingles in adults.
A comprehensive understanding of VZV’s long-term effects, transmission routes, and the significance of vaccination is essential for effective herpes prevention and public health education initiatives.
The dual nature of this virus underscores the necessity for a holistic approach to public health, highlighting the importance of vaccination not only during childhood but also in adulthood.
Given that shingles can result in painful complications and prolonged discomfort, it is imperative to raise awareness regarding its association with VZV.
Various educational resources, such as community workshops and informative campaigns, are instrumental in disseminating knowledge to the public.
By elucidating the implications of VZV and its connection to the herpesvirus family, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the importance of preventive measures, which may lead to increased vaccination rates and a decrease in outbreaks.
How is herpes transmitted?

Herpes transmission occurs through several routes, including sexual contact and skin-to-skin contact. Understanding these pathways is essential for effective infection control.
Both asymptomatic herpes and active outbreaks play a role in the spread of the virus, highlighting the need for education regarding viral shedding and the significance of safe sex practices among sexual partners.
1. Sexual contact
Sexual contact is a primary mode of transmission for herpes, specifically HSV-1 and HSV-2, which can be spread through intimate interactions, including oral, vaginal, and anal sex.
Comprehending this mode of transmission is essential for implementing safe sex practices and facilitating effective communication between partners to mitigate the risks associated with sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Partners should participate in open discussions regarding their sexual histories, potential symptoms, and any known infections. This approach fosters mutual trust and alleviates anxiety related to transmission.
The consistent use of condoms is a critical strategy that significantly reduces the likelihood of herpes transmission – however, it is important to note that condoms do not offer complete protection, particularly for areas not covered by the condom.
Awareness of outbreak triggers and the avoidance of sexual contact during these periods can further enhance protection for partners.
Education regarding herpes is vital, as it enables individuals to make informed decisions and adopt practices that promote sexual health and safety.
2. Skin-to-skin contact
Herpes can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, allowing the virus to spread even in the absence of visible symptoms.
This emphasizes the importance of understanding asymptomatic herpes and highlights the need for effective outbreak management and awareness initiatives to reduce infection rates.
Many individuals may be unaware that they are carriers of the virus, which significantly increases the potential for unintentional transmission.
Therefore, it is crucial for everyone to remain vigilant regarding their health status.
Awareness campaigns and education about the dynamics of the virus, particularly concerning asymptomatic shedding, are essential.
Implementing strategies such as consistent condom use, regular testing, and open communication with partners can greatly diminish the likelihood of herpes transmission.
By fostering an environment where individuals feel enableed to discuss their status and preventative measures, society can collectively work toward reducing the stigma associated with the virus and enhancing overall sexual health.
3. Sharing personal items
Sharing personal items, such as towels, razors, or lip balm, can increase the risk of herpes transmission, particularly during active outbreaks.
It is essential to acknowledge the associated risks of sharing personal items in order to implement effective infection prevention strategies and enhance public awareness regarding the routes of herpes transmission.
Moreover, the importance of personal hygiene in this context cannot be overstated. Individuals should take proactive measures to maintain cleanliness and thereby minimize their exposure to the herpes virus.
Regular handwashing, refraining from sharing items that come into direct contact with the skin, and adopting safe practices are critical components of this preventive approach.
Awareness campaigns are vital tools for educating the public about these measures, as they help to clarify misconceptions about the virus and encourage responsible behavior.
By promoting a culture of hygiene and awareness, communities can significantly mitigate the risks associated with herpes and foster overall health.
What are the symptoms of herpes?
Herpes symptoms can vary considerably among individuals, typically presenting as painful genital lesions, oral lesions, and flu-like symptoms during the initial outbreak.
A comprehensive understanding of these symptoms, along with the ability to identify potential outbreak triggers, can enhance awareness and facilitate effective management of herpes.
This, in turn, can significantly improve an individual’s quality of life.
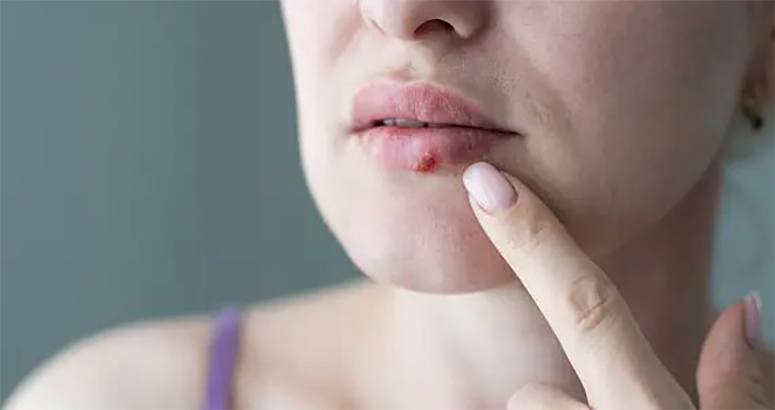
1. Blister-like sores
Blister-like sores are a characteristic symptom of herpes infections, typically manifesting during the initial outbreak and potentially recurring in subsequent episodes.
These lesions may develop on various parts of the body, particularly in instances of genital herpes, highlighting the importance of effective outbreak management and symptom recognition.
The sores often present as painful blisters that can cluster together and may be associated with itching, burning sensations, or flu-like symptoms.
Common locations for these lesions include the genitals, buttocks, and thighs in cases of genital herpes, while oral herpes may affect the lips or the oral cavity.
It is imperative for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek prompt medical advice, as early intervention can help prevent complications and mitigate transmission risks.
Implementing effective symptom management strategies, such as antiviral medications, lifestyle modifications, and comfort measures, can significantly alleviate discomfort and enhance overall quality of life.
2. Flu-like symptoms
Flu-like symptoms, such as fever, swollen lymph nodes, and fatigue, may accompany the initial outbreak of herpes and can vary in intensity among individuals.
These symptoms reflect the immune system’s response to the viral infection, highlighting the necessity of recognizing them for prompt diagnosis and management.
The immune system’s reaction underscores its essential role in combating the herpes simplex virus – however, when the immune response falters or becomes overwhelmed, complications may develop.
For many individuals, the simultaneous occurrence of these flu-like symptoms can be distressing, leading to confusion and concern regarding their health.
Access to healthcare is crucial, as timely intervention can alleviate both physical discomfort and the emotional stress associated with the diagnosis.
Understanding these relationships emphasizes the importance of proactive health management, ensuring that individuals seek appropriate care to effectively navigate the complexities surrounding herpes outbreaks.
3. Itching or burning sensation
An itching or burning sensation in the affected areas is frequently one of the initial warning signs of a herpes outbreak, indicating the potential onset of lesions.
Early recognition of these sensations can be critical in preventing infection and managing outbreaks for individuals at risk.
Being aware of these symptoms enables individuals to take proactive measures, such as reducing sexual activity during these phases and considering topical treatments to alleviate discomfort.
Effective management may also include maintaining a robust immune system through a balanced diet and adequate hydration.
Consulting a healthcare professional is essential, as they can provide personalized advice and recommend antiviral medications to decrease the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
Addressing these early warning signs not only assists in managing immediate symptoms but also enhances an individual’s sense of control and enablement regarding their health.
What are the risk factors for contracting herpes?
Multiple risk factors contribute to the likelihood of contracting herpes, including engaging in sexual activity with multiple partners, insufficient implementation of herpes prevention strategies, and the presence of a weakened immune system.
Recognizing and understanding these risk factors is crucial for public health initiatives focused on reducing the transmission of herpes and promoting awareness regarding responsible sexual behavior.
1. Age
Age is a significant determinant of herpes risk, with younger individuals often demonstrating higher rates of infection due to increased sexual activity and varying levels of awareness regarding safe sex practices.
Understanding the influence of age on herpes transmission can inform public health initiatives and educational efforts aimed at reducing infection rates.
As young individuals navigate their formative years, they frequently engage in exploratory behaviors that may unfortunately heighten their risk of infection. This demographic often lacks access to comprehensive sexual health education, rendering them susceptible to misinformation.
Integrating discussions about oral and genital herpes into health curricula enables youth to make informed decisions regarding their sexual health.
Raising awareness about the risks associated with herpes – particularly among teenagers and young adults – presents a critical opportunity to instill lifelong habits that prioritize safety, ultimately contributing to the reduction of herpes transmission within this age group.
2. Sexual activity
Engaging in sexual activity with multiple partners increases the risk of herpes transmission, thereby underscoring the necessity for comprehensive sexual histories and responsible sexual behaviors.
This situation emphasizes the critical importance of open communication between partners regarding sexual health.
In any relationship, discussing past sexual experiences and STI statuses enables individuals to make informed decisions that prioritize their well-being.
Implementing safe sex practices, such as consistent condom usage and regular testing for herpes and other STIs, can significantly mitigate the risk of transmission.
By fostering a culture of transparency and mutual respect in intimate relationships, individuals not only safeguard their own health but also that of their partners, contributing to the promotion of a healthier sexual community overall.
3. Weakened immune system
Individuals with a compromised immune system face a heightened risk of contracting herpes and experiencing severe outbreaks due to their body’s diminished ability to control viral infections.
Recognizing this risk factor emphasizes the necessity for proactive infection prevention strategies and enhanced healthcare access for vulnerable populations.
Those affected frequently encounter not only the physical challenges associated with recurrent outbreaks but also the emotional and psychological burdens that accompany them.
This situation underscores the importance of regular healthcare support and monitoring, as well as the implementation of effective preventive measures, including vaccination and antiviral therapies.
Promoting awareness and education regarding this susceptibility can enable at-risk individuals to take appropriate precautions and seek timely medical intervention.
By prioritizing healthcare resources and implementing tailored prevention strategies, communities can substantially reduce the incidence and severity of herpes infections among individuals with weakened immune systems.
How can you reduce the odds of getting herpes?
Reducing the likelihood of contracting herpes necessitates the implementation of effective prevention strategies, such as practicing safe sex and understanding the efficacy of condoms in minimizing transmission risks.
Awareness and education are critical components in managing outbreaks and promoting responsible sexual behavior among individuals and their partners.
1. Practicing safe sex
Practicing safe sex through the use of condoms and dental dams can significantly reduce the risk of herpes transmission, thereby providing a valuable layer of protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Effective communication between partners regarding sexual health and herpes status is crucial for the implementation of successful prevention strategies.
By prioritizing these safe sex practices, individuals not only protect themselves from potential infections but also cultivate an environment of trust and understanding within their relationships.
Engaging in open and honest discussions about sexual history enables both partners to make informed decisions, ensuring that all parties are cognizant of the associated risks.
Barrier methods, such as condoms, have been proven to be highly effective in minimizing the transmission of herpes as well as a wide range of STIs, thereby enhancing overall sexual health.
Ultimately, integrating these practices into one’s lifestyle contributes to a healthier society by reducing infection rates and promoting responsible sexual behavior.
2. Avoiding skin-to-skin contact
Avoiding skin-to-skin contact during outbreaks or when symptoms are present is essential for the prevention of herpes, as this significantly minimizes transmission risks.
Recognizing the importance of infection control during these periods is crucial for effective outbreak management.
This practice not only helps safeguard partners from potential exposure but also constitutes a fundamental component of a comprehensive strategy for managing herpes.
Maintaining open communication with partners regarding outbreaks, symptoms, and prevention methods enables both individuals to take necessary precautions.
Furthermore, utilizing barrier methods such as condoms, even in the absence of visible symptoms, further reduces the risk of transmission and contributes to a healthier sexual relationship.
By prioritizing these strategies, individuals can play a pivotal role in curbing the spread of herpes, ultimately fostering a more informed and responsible approach to sexual health.
3. Not sharing personal items
Avoiding the sharing of personal items, such as towels or utensils, is a critical component of herpes prevention, as it significantly reduces the likelihood of transmission even in the absence of visible symptoms.
Promoting public awareness of this practice is essential for effective infection control.
This approach not only protects individual health but also contributes to the overall well-being of the community by minimizing the spread of infections.
Public awareness campaigns are instrumental in educating individuals about the risks associated with sharing personal items and the potential for asymptomatic transmission.
Utilizing various platforms, these initiatives disseminate crucial information that underscores the importance of maintaining consistent personal hygiene practices.
By cultivating a culture of awareness and responsibility, communities can collectively enhance their defenses against herpes and other communicable diseases.
Educational resources should emphasize the necessity of personal responsibility and encourage open discussions regarding sexual health to dispel myths and promote safe practices.
Learn more about the probability of getting herpes by viewing our FAQ further down this page.
Dive into the fascinating realm of probabilities and remarkable events. Satisfy your curiosity and enhance your understanding by exploring our articles at WhatAreTheOddsOf.NET.



