Contents
Colonoscopy is a critical medical procedure that significantly contributes to the detection and prevention of colorectal cancer and various gastrointestinal disorders.
While the procedure is generally safe, many patients express concerns regarding the potential risks involved, including the rare occurrence of severe complications or death.
Understanding what are the odds of dying from a colonoscopy are can help alleviate some of these concerns.
This article aims to elucidate what a colonoscopy entails, the reasons for its performance, common indications for the procedure, and the associated risks.
Additionally, we will discuss strategies to minimize these risks and promote a safer experience.
The objective is to provide comprehensive information on this essential topic, thereby equipping individuals with the knowledge necessary for well-considered choices.
What is a colonoscopy?
A colonoscopy is a medical procedure that enables healthcare professionals to inspect the interior of the gastrointestinal tract, specifically the colon and rectum, utilizing a flexible tube equipped with a camera.
This outpatient procedure is crucial for the early detection and prevention of colorectal cancer, as well as for diagnosing a range of gastrointestinal disorders.
By adhering to established medical guidelines, patients can enhance their safety and improve overall health outcomes.
Why is a colonoscopy performed?
Colonoscopy is conducted for a variety of purposes, primarily to screen for colorectal cancer, identify bowel abnormalities, and evaluate gastrointestinal symptoms.
Medical professionals recommend this procedure based on an individual’s health status, age, and medical history, as it is instrumental in mitigating health risks associated with colorectal diseases.
What are the common reasons for a colonoscopy?
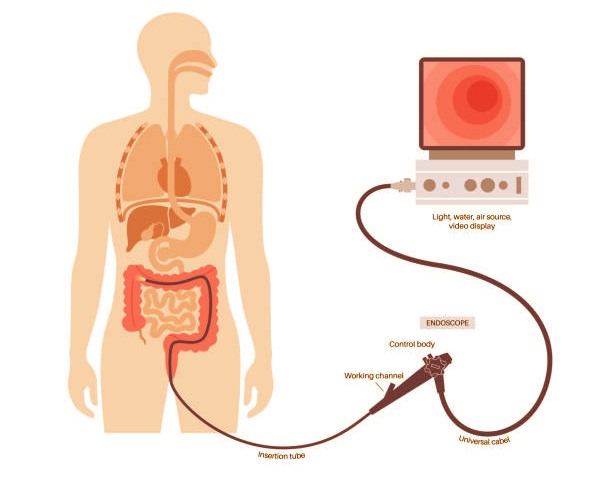
Common indications for undergoing a colonoscopy include screening for colorectal cancer, investigating gastrointestinal symptoms such as bleeding, abdominal pain, or alterations in bowel habits, and the removal of polyps that may have the potential to develop into cancer.
Healthcare providers frequently recommend this procedure as a preventive measure or to further assess concerning symptoms.
The significance of such screenings is paramount, as research indicates that early detection through colonoscopy can decrease colorectal cancer mortality by as much as 68%.
The American Cancer Society reports that nearly 1 in 24 individuals will develop colorectal cancer during their lifetime, underscoring the vital role of patient education in raising awareness about the importance of this diagnostic intervention.
By understanding risk factors, screening guidelines, and the role of polyps in cancer progression, patients are better equipped to make informed decisions regarding their health.
Healthcare practitioners advocate for a proactive approach to gastrointestinal health, emphasizing the necessity of regular screenings not only for symptomatic individuals but also for those within recommended age groups, thereby promoting early intervention and potentially saving lives.
What are the risks of a colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy is widely regarded as a safe medical procedure – however, it is important for patients to be aware of certain risks and potential complications associated with it.
These risks may include bleeding, bowel perforation, infection, and adverse events related to anesthesia and sedation, which, although rare, could potentially lead to mortality.
A thorough understanding of these risks is crucial for patients to make informed decisions regarding the procedure.
What are the possible complications of a colonoscopy?
Possible complications of a colonoscopy can vary in severity, with bleeding, bowel perforation, and infection being among the most critical concerns.
Understanding these complications is essential for managing patient expectations and ensuring safety during the procedure.
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in identifying and addressing these risks, underscoring the importance of comprehensive pre-procedural assessments.
For instance, the occurrence of bleeding is often associated with the removal of polyps or other tissue during the examination.
Effective management strategies, including diligent monitoring following the procedure and prompt intervention should symptoms arise, are of paramount importance.
Bowel perforation, although infrequent, requires immediate medical intervention, as it can result in serious complications if not treated promptly.
Infections, while also uncommon, warrant appropriate prophylactic measures and thorough patient education prior to the colonoscopy, thereby reinforcing the healthcare team’s commitment to procedural safety and optimal patient care.
Are there any pre-existing conditions that increase the risk of complications?
Certain pre-existing conditions can elevate the risk of complications during a colonoscopy, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and various gastrointestinal disorders.
It is imperative for patients to provide their healthcare providers with a complete and accurate medical history to enable a comprehensive clinical risk assessment and the implementation of appropriate precautions.
For example, individuals with cardiovascular concerns may face increased risks related to sedation, while the management of diabetes can complicate pre-procedure fasting requirements.
Understanding the interplay between these conditions and the colonoscopy process is essential for ensuring patient safety.
Healthcare providers should prioritize detailed discussions regarding existing health issues, as this information is crucial for tailoring preparation and post-procedure care.
Additionally, patient education is of utmost importance – individuals must be informed about the implications of their pre-existing conditions to enable them to participate actively in their healthcare decisions, thereby facilitating a smoother clinical experience.
What are the odds of dying from a colonoscopy?
The likelihood of mortality associated with a colonoscopy is regarded as low, with mortality rates typically estimated to be between 1 in 15,000 and 1 in 30,000 procedures.
These rates can vary based on several risk factors, including age, overall health status, and the existence of underlying medical conditions.
A statistical analysis of healthcare outcomes serves to contextualize these figures and facilitates well-considered choices for patients considering the procedure.
Understanding what are the odds of dying from a colonoscopy helps to put these numbers into perspective and can reduce patient anxiety.
What are the factors that affect the risk of death during a colonoscopy?
Several factors can influence the risk of mortality during a colonoscopy, including the patient’s age, overall health status, and specific medical history.
Older patients or those with significant comorbid conditions may face elevated risks, which underscores the necessity for a personalized approach to risk assessment and patient care.
For example, a patient with a history of heart disease or respiratory issues may experience complications that younger, healthier individuals typically do not encounter.
Additionally, demographic variables such as gender, socioeconomic status, and ethnicity can also impact overall health outcomes.
Customized healthcare interventions that take these individual factors into account are essential not only for minimizing risks but also for enhancing patient trust and compliance with recommended follow-up care.
By adhering to principles of medical ethics, healthcare providers can ensure that patients are comprehensively informed about the risks and benefits pertinent to their specific demographics, thereby fostering a more equitable and compassionate healthcare environment.
How can the risk of death during a colonoscopy be reduced?
Minimizing the risk of mortality during a colonoscopy entails implementing several essential measures before, during, and after the procedure, with a steadfast commitment to prioritizing patient safety at all times.
Adequate preparation, which includes dietary modifications and adjustments to medication, along with vigilant monitoring during sedation and comprehensive follow-up care, can significantly improve patient outcomes.
What precautions can be taken before the procedure?
Ahead of undergoing a colonoscopy, patients should take several precautions to minimize risks, including adherence to dietary restrictions, compliance with specific medication guidelines, and participation in comprehensive patient education regarding the procedure.
Addressing questions like “what are the odds of dying from a colonoscopy” starts with thorough preparation. These preparations are critical for ensuring a safe and effective colonoscopy experience. It is also imperative for individuals to engage in appropriate health assessments before the appointment.
This may involve a thorough review of the patient’s medical history and current medications, as well as a discussion of any pre-existing health conditions.
Adherence to these steps not only helps to reduce the likelihood of potential complications but also assists healthcare providers in devising the most suitable approach for each patient.
Implementing preventive measures, such as refraining from anti-inflammatory drugs or blood thinners in the days leading up to the procedure, significantly enhances patient safety and contributes to improved outcomes.
What can be done during the procedure to reduce the risk of death?
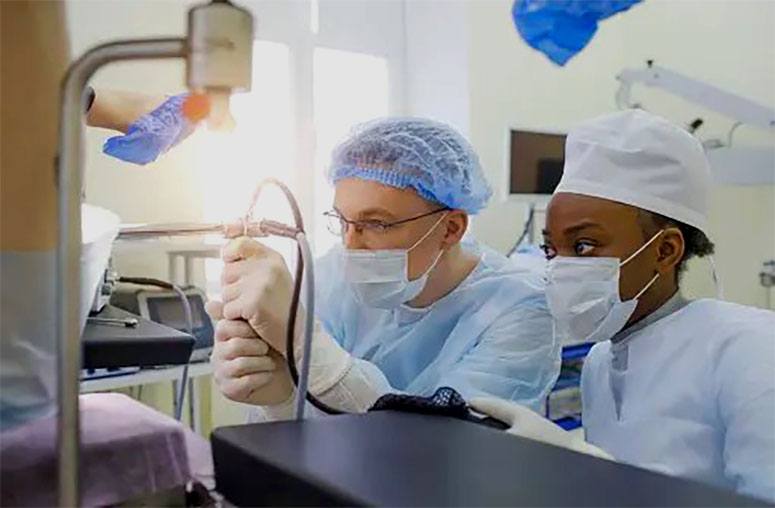
During a colonoscopy, healthcare professionals can implement various strategies to mitigate the risk of mortality, including meticulous monitoring of anesthesia levels, employing experienced personnel, and utilizing advanced endoscopic technologies.
Ensuring patient safety throughout the procedure is essential for achieving favorable health outcomes.
Furthermore, additional measures such as comprehensive pre-procedural assessments and effective communication among team members can significantly enhance the overall safety of the procedure.
By thoroughly reviewing patients’ medical histories and identifying potential contraindications, healthcare professionals can customize their approaches to meet individual needs.
The establishment of protocols for real-time monitoring of vital signs facilitates the prompt recognition and intervention in the event of any emerging complications.
Additionally, ongoing training and education for the medical team in the latest techniques and equipment are crucial, as these practices contribute to improved patient outcomes and foster an environment in which individuals feel cared for and supported.
What can be done after the procedure to reduce the risk of death?
Post-procedure care is essential for minimizing the risks associated with colonoscopy.
This includes appropriate monitoring for signs of complications, conducting follow-up assessments to evaluate patient recovery, and offering necessary support.
Effective health monitoring after the procedure contributes to improved patient outcomes and heightened satisfaction.
Patients often ask, “what are the odds of dying from a colonoscopy” and knowing that there are structured post-procedure measures in place can provide reassurance.
Following a colonoscopy, it is imperative to maintain open lines of communication between healthcare providers and patients to address any concerns that may arise.
This may involve scheduled phone calls or follow-up appointments to assess the healing process and ensure patients feel supported throughout their recovery journey.
Educating patients about potential warning signs, such as abnormal pain or changes in bowel habits, enables them to seek assistance in a timely manner.
Additionally, providing resources for mental and emotional support can enhance the overall patient experience, fostering trust and ensuring that individuals feel cared for during their recovery phase.
Details about the odds of dying from a colonoscopy are available in our FAQ further down this page.
Delve into the intriguing field of probabilities and extraordinary events. Discover more by reading our articles at WhatAreTheOddsOf.NET.