Contents
- 1 What is a liver donor?
- 2 Why is liver donation important?
- 3 What are the odds of being a match for a liver donor?
- 4 What are the different types of liver donation?
- 5 What are the steps to becoming a liver donor?
- 6 What are the risks and complications of liver donation?
- 7 How can someone increase their chances of being a match for a liver donor?
- 8 What are the alternatives to liver donation?
In the realm of organ transplantation, liver donation is a vital component in saving lives and enhancing the quality of life for individuals afflicted with liver diseases.
It is essential to comprehend the significance of being a liver donor, the critical nature of donation, and the likelihood of identifying a compatible match, as this knowledge enables individuals to make informed decisions.
What are the odds of being a match for a liver donor? Understanding this aspect is crucial for potential donors and recipients alike.
This article examines the various types of liver donations, the process of becoming a donor, and the associated risks, while also evaluating alternative treatment options.
We invite you to explore the fundamental aspects of liver donation and its profound impact on patients and their families.
What is a liver donor?
A liver donor is an individual who donates a portion of their liver, or their entire liver, for transplantation to another person experiencing liver disease or liver failure.
Donations may originate from living donors, who can provide a segment of their healthy liver, or from deceased donors who have consented to organ donation post-mortem.
The liver possesses a remarkable ability to regenerate, enabling living donors to achieve complete recovery while simultaneously saving the life of a recipient in need.
It is crucial to comprehend the criteria for liver donation to ensure the success of the organ transplant.
Why is liver donation important?
Liver donation is of paramount importance as it offers life-saving treatment for individuals suffering from severe liver disease, thereby addressing the critical organ shortage faced in numerous regions.
As chronic liver disease continues to rise, the demand for liver transplants has become increasingly urgent, often resulting in patients remaining on extensive transplant waiting lists.
Organ donation not only enhances survival rates but also significantly improves the quality of life for recipients.
Raising awareness regarding liver donation can motivate more individuals to register as donors, thereby alleviating some of the pressures on organ allocation systems.
Statistically, liver disease ranks among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with thousands of lives lost annually due to complications associated with conditions such as cirrhosis and hepatitis.
Recent reports indicate that over 14,000 individuals in the United States are currently awaiting liver transplants, underscoring the pressing need for additional donors.
The ethical implications surrounding organ donation are critical, as individuals must carefully consider their choices within the framework of societal values and medical guidelines.
Public awareness campaigns are essential in educating communities about the significance of liver donations, dispelling prevalent myths, and encouraging others to join the donor registry.
Such efforts ultimately contribute to fostering a culture of generosity and hope that has the potential to transform lives.
What are the odds of being a match for a liver donor?
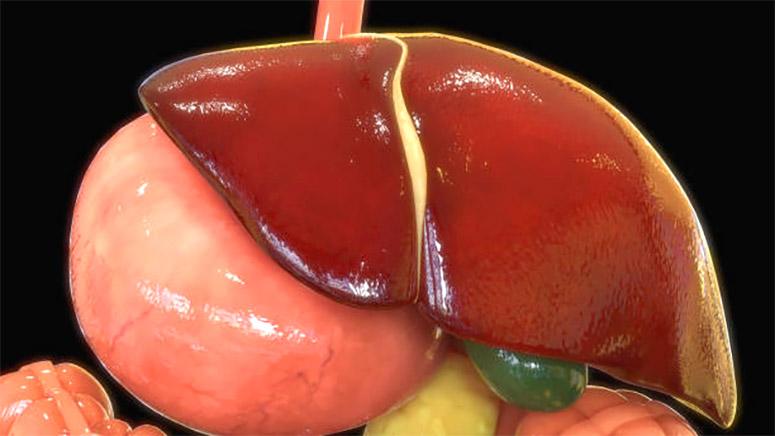
The likelihood of being a suitable match for a liver donor is contingent upon several critical factors, including blood type, HLA typing, and overall organ compatibility.
A successful donor-recipient pairing is imperative to ensure the optimal functioning of the transplanted liver within the recipient’s body.
Medical professionals perform comprehensive compatibility testing, which evaluates various matching criteria to identify the most appropriate candidate for a liver transplant.
A clear understanding of these factors can assist patients and potential donors in navigating the complexities associated with the organ matching process.
What factors affect liver donation compatibility?
Several factors significantly influence liver donation compatibility, with matching criteria such as blood type and HLA typing being of paramount importance.
These elements are essential in ensuring the dropped liver will function optimally within the recipient’s body. Additionally, factors such as age, medical history, and tissue typing are considered during the evaluation process to assess overall transplant eligibility.
A comprehensive understanding of these compatibility factors can greatly enhance the prospects of a successful organ transplant.
Blood type is a fundamental criterion, as a mismatch may lead to severe complications, including organ rejection. HLA typing further refines the compatibility assessment by identifying specific markers present on the liver and the recipient’s immune cells, thereby facilitating a more precise match.
This intricate matching process not only increases the likelihood of the transplanted organ being accepted but also significantly contributes to optimizing surgical outcomes.
The greater the compatibility, the more effectively post-operative care can proceed, potentially reducing the risk of infections and the necessity for intensive immunosuppressive therapy, ultimately enhancing recovery and long-term health.
What are the different types of liver donation?
There are two primary modalities of liver donation – living donor liver transplants and deceased donor liver transplants.
Living donor liver transplants involve a healthy individual donating a segment of their liver, whereas deceased donor liver transplants utilize organs from individuals who have consented to organ donation post-mortem.
Each type of donation presents distinct advantages and considerations, particularly concerning the timely availability of donor organs and the health outcomes for recipients.
It is essential for both potential donors and recipients to understand these options as they navigate the transplant process.
1. Living donor liver transplant
Living donor liver transplants involve a healthy individual donating a portion of their liver to a recipient in need, thereby providing a crucial option in the context of organ scarcity.
This type of transplant facilitates a scheduled surgical procedure, which can result in improved surgical outcomes and a reduced waiting time for the recipient.
Before the donation, the living donor undergoes a comprehensive health assessment to ensure their safety during the surgical procedure and to promote a successful recovery afterward.
This evaluation typically encompasses extensive medical testing, psychological assessments, and consultations with specialists to ascertain that the donor is both physically and mentally prepared for the surgery.
During the surgical procedure, surgeons meticulously excise a segment of the donor’s liver, employing minimally invasive techniques when feasible to minimize recovery time and discomfort.
Once transplanted, the liver possesses a remarkable ability to regenerate, benefiting both the donor and the recipient.
Post-operative care is essential for the donor, generally involving regular follow-up appointments to monitor liver function and overall health.
Living donation significantly enhances transplant success rates and improves long-term outcomes, providing recipients not only with a second chance at life but also fostering a closer bond between the donor and the recipient.
2. Deceased donor liver transplant
Deceased donor liver transplants involve the utilization of organs from individuals who have consented to organ donation following their death, representing a crucial aspect of the organ transplant landscape.
This type of transplant is frequently performed in emergency situations, particularly when the recipient is at significant risk due to liver failure.
The process encompasses complex organ procurement and transplant procedures, with the objective of maximizing transplant success and improving patient outcomes.
The intricacies of this process are considerable, necessitating meticulous coordination among hospitals, organ procurement organizations, and surgical teams.
Each phase, from the identification of potential donors to the matching with recipients, demands rigorous attention to detail to ensure that the organs are viable and suitable for transplantation.
Furthermore, ethical dilemmas arise, particularly concerning consent and the allocation of limited resources, which prompt important questions regarding fairness and transparency within the transplant process.
Continuous advancements in medical research, including enhanced preservation techniques and improved immunosuppressive therapies, are progressively refining the metrics used to evaluate transplant success, such as graft survival rates and long-term patient health outcomes.
What are the steps to becoming a liver donor?
The process of becoming a liver donor involves a comprehensive procedure designed to ensure the safety and health of both the donor and the recipient. Initially, potential donors undergo a preliminary screening to ascertain their eligibility.
This is followed by an extensive clinical evaluation that examines their medical history and overall health status.
This thorough health assessment is essential in determining the donor’s ability to undergo surgery and effectively participate in the donor matching process.
1. Initial screening
The initial screening process for potential liver donors is of paramount importance, as it aids in identifying individuals who may be suitable for organ donation.
This screening encompasses a comprehensive review of the donor’s medical history, an assessment of their overall health, and an evaluation of any potential risks associated with the donation.
It serves as the preliminary step in the donor matching process, ensuring that the selected donor fulfills the necessary transplant eligibility criteria.
During the initial screening, healthcare professionals will conduct a series of specific tests, including blood tests, imaging studies such as ultrasounds or CT scans, and psychological evaluations to assess the donor’s mental readiness.
The results of these assessments play a crucial role in determining not only the donor’s physical suitability but also their capacity to manage the emotional and psychological aspects of the donation process.
This comprehensive health assessment is essential, as it establishes the foundation for ensuring that the organ transplantation proceeds smoothly, thereby minimizing complications for both the donor and the recipient.
Consequently, a meticulous initial screening can significantly enhance the effectiveness of the entire donor matching process.
2. Evaluation process
The evaluation process for potential liver donors involves a comprehensive clinical assessment to determine their medical eligibility for donation.
During this stage, medical professionals conduct liver function tests and various diagnostic evaluations to ascertain the overall health of the donor and the suitability of their liver for transplantation.
This meticulous approach is essential to ensure the safety of both the donor and the recipient throughout the transplant process.
These evaluations often include imaging studies, such as ultrasounds or CT scans, to visualize liver anatomy and identify any abnormalities that may affect the donor’s capability.
Additionally, assessments of blood type compatibility and infectious disease screening are conducted, which are critical for matching a donor with the intended recipient.
All of these steps are foundational to the donor matching process, significantly increasing the likelihood of successful transplantation and minimizing potential complications post-surgery.
By thoroughly examining these components, healthcare professionals are able to make informed decisions that enhance the prospects of a favorable outcome for all parties involved.
3. Surgery and recovery
The surgical procedure for liver donation entails a comprehensive process in which a portion of the donor’s liver is surgically removed and subsequently transplanted into the recipient.
This donor surgery is highly specialized and necessitates the expertise of skilled medical professionals to ensure optimal surgical outcomes.
Post-operative care for the donor is equally critical, as it involves the monitoring of recovery and the management of any potential complications that may arise during the healing process.
During the surgical procedure, the donor typically undergoes either a laparoscopic or open surgery technique, with the choice depending on the specific circumstances and health status of the donor.
Following the surgery, the donor can anticipate a significant recovery period, which often spans several weeks, during which the liver will regenerate and resume normal function.
Medical teams closely monitor vital signs and conduct liver function tests to mitigate the risk of complications, such as infection or bleeding.
Additionally, psychological support for donors is essential, as the emotional implications of the donation process can influence overall recovery.
Establishing a comprehensive follow-up care plan is vital for not only facilitating physical healing but also addressing any emotional concerns, thereby contributing to a successful outcome for both the donor and the recipient.
What are the risks and complications of liver donation?
Liver donation is a profoundly life-saving act – however, it entails certain risks and potential complications that donors must be cognizant of.
These risks may include surgical complications, challenges during recovery, and long-term health implications. Implementing proper post-operative care and monitoring is essential to mitigate these risks and facilitate a smooth recovery process for the donor.
Conducting a thorough health assessment prior to the donation can also aid in identifying any factors that may elevate the risk of complications.
It is imperative for potential donors to understand the nature of these risks – they should be well-informed regarding what to expect during the donation process and the subsequent healing period.
Potential complications can encompass a range of issues, from infection and bleeding to concerns related to liver function following surgery.
Medical professionals play a critical role in educating donors about these risks and providing support throughout every stage of the recovery journey.
This support includes tailored recovery plans, follow-up appointments, and access to mental health resources to assist donors in adapting to the physical and emotional changes that may arise post-donation.
How can someone increase their chances of being a match for a liver donor?
Increasing the likelihood of being a match for a liver donor involves several proactive measures that individuals can undertake, including the maintenance of a healthy lifestyle and registering as an organ donor.
Adopting healthy habits can improve overall health, which is essential for meeting transplant eligibility criteria.
Furthermore, educating oneself about the donation process and actively advocating for organ donation can significantly enhance the chances of finding a suitable donor match.
1. Maintain a healthy lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for individuals seeking to enhance their eligibility as candidates for liver donation.
A balanced diet, regular exercise, and the avoidance of harmful substances significantly contribute to liver health and overall well-being.
This proactive approach not only improves an individual’s quality of life but also aligns with the criteria for transplant eligibility, rendering them a more viable candidate for organ donation.
Consuming a diverse array of nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, is vital for nourishing the liver.
Incorporating exercise routines, whether they involve strength training or aerobic activities, is important for managing weight and improving metabolic functions.
It is also crucial to avoid excessive alcohol consumption and harmful drugs, as these can lead to liver damage.
Regular health assessments play a significant role in monitoring liver function and overall health status, ensuring that individuals remain informed about their compatibility for future liver donation opportunities.
2. Register as an Organ Donor
Registering as an organ donor is a crucial step that individuals can undertake to enhance their likelihood of being a match for liver donation. This act signifies a commitment to saving lives and facilitates the donor matching process. By enrolling in an organ donor registry, individuals can ensure that their wishes are clearly articulated and respected, thereby contributing to the overall awareness and advocacy for organ donation.
To initiate the registration process, one may visit a local Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) or utilize online platforms that provide a straightforward and user-friendly application process. It is essential for potential donors to review the requirements and fully understand the implications of being an organ donor, as this promotes well-considered choices.
Donor advocacy plays a pivotal role in raising awareness, making it imperative for communities to engage in discussions regarding the significance of organ donation. Public awareness campaigns are fundamental, not only in encouraging individuals to register but also in dispelling myths surrounding organ donation, thus fostering a culture of generosity and hope.
3. Consider living donation
Considering living liver donation can significantly enhance the likelihood of identifying a suitable donor match for individuals in need of a transplant.
Living donation enables individuals to take an active role in the transplant process, often resulting in improved surgical outcomes for recipients.
Advocating for donors and raising awareness about living donation within the transplant community can further promote this lifesaving option.
This proactive approach not only increases survival rates for recipients but also provides potential donors with a profound sense of fulfillment from their altruistic decision.
It is essential for communities to comprehend the positive impact of living donations, as misunderstandings can frequently discourage willing donors.
Through targeted educational programs and outreach initiatives, individuals can be equipped with the necessary knowledge to make informed decisions regarding donation.
The collaboration of healthcare organizations, community leaders, and transplant recipients in these initiatives can foster a supportive environment that prioritizes and normalizes living liver donation, ultimately leading to the preservation of more lives.
What are the alternatives to liver donation?

Liver donation is an essential solution for individuals suffering from severe liver disease – however, it is important to consider alternative options that may support liver function and overall health.
Approaches such as artificial liver support systems, pharmaceutical interventions, and lifestyle modifications can offer significant assistance in managing liver conditions.
By understanding these alternatives, patients can explore comprehensive strategies for maintaining their liver health and potentially avoiding the necessity for a transplant.
1. Artificial liver support
Artificial liver support systems are sophisticated medical technologies developed to provide temporary assistance to patients with compromised liver function.
These systems can facilitate a bridge to transplantation or support the liver in regaining its functionality, thereby affording critical time for patients experiencing acute liver failure.
By utilizing artificial liver support, patients may achieve improved health outcomes and prolong their time while awaiting a suitable donor match.
The underlying mechanisms of these technologies typically involve detoxification processes and bioartificial liver support, which utilize living liver cells to perform functions akin to those of a healthy liver.
Recent advancements in medical technology have significantly improved the efficacy of these systems, delivering enhanced filtration and metabolic support during critical periods.
This innovative approach not only stabilizes patients but may also yield better post-transplant outcomes when compared to traditional care methods.
Innovations such as enhanced bioreactor designs and optimized patient management protocols continue to refine the integration of these systems with established transplantation options, ultimately transforming the treatment landscape for individuals with severe liver conditions.
2. Medication and lifestyle changes
Medications and lifestyle modifications are essential elements in the management of liver health and can serve as effective alternatives to surgical interventions for certain patients.
By adhering to prescribed medication regimens and implementing positive lifestyle changes, individuals can often stabilize their liver function and enhance their overall well-being.
Patient education is critical in enabling individuals to comprehend these alternatives and make informed health decisions.
Incorporating specific medications, such as antiviral agents for hepatitis or dietary supplements like milk thistle, can improve liver function.
Additionally, dietary modifications – such as prioritizing whole foods, reducing sugar intake, and ensuring adequate hydration—offer substantial benefits.
Regular physical activity not only assists in maintaining a healthy weight but also enhances overall metabolic health, thus alleviating some of the stress on the liver.
It is imperative to avoid alcohol and certain over-the-counter medications that may place additional strain on this vital organ. For many individuals, participation in support groups or educational programs can foster a deeper understanding of their liver conditions and encourage the adoption of healthier long-term habits.
For information on the likelihood of being a match for a liver donor, please see our FAQ further down the page.
Enter the captivating realm of probabilities and remarkable events. Enhance your curiosity and knowledge with our comprehensive articles at WhatAreTheOddsOf.NET.